Tech:Electrical/Starter Motor/Characteristics
Characteristics
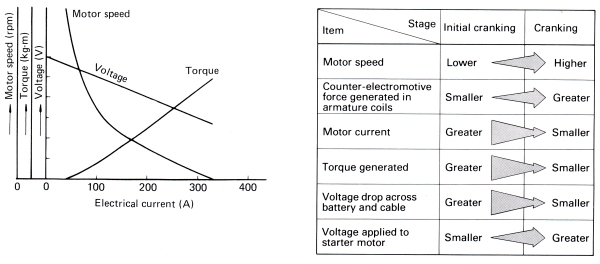
The DC series motor used in a starter motor has the following operational characteristics:
- The heavier the current drawn by the starter motor, The greater the torque generated by the motor.
- The faster the motor speed, The greater the counter-electromotive force generated by the armature coils and the less current that flows.
At the initial engine cranking stage when the motor speed is low, The armature coils generate a smaller counter-electromotive force. As a result, A great amount of current flows through the motor and generates a large torque. However, The voltage drops across the battery terminals and starter cable increase greatly due to this heavy current draw, The resistance of the cable, And the internal resistance of the battery, So the voltage actually applied to the motor is low.
As the motor speeds up, It generates a greater counter-electromotive force and thus draws less current. As a result, The voltage drops across the battery terminals and starter cable decrease, So the voltage applied to the starter motor increases. The output torque, However, Drops.
The final engine cranking speed is that where the torque generated by the starter motor as it rotates equals that required to crank the engine.
The torque required to crank the engine is greatest at the initial engine cranking stage, When the rotational speed is the smallest. Less torque, However, Is necessary once the engine has built up a constant speed. The DC series motor therefore provides the torque characteristics best suited for a starter motor.
Back to Starter Motor
Back to Main Page